First-Time Homebuyers Face Shifting Market, Stress, Struggles: New Survey
A new survey of 1,000 first-time homebuyers reveals the complex and often stressful reality of entering the housing market. Rising housing prices, high interest rates, and market uncertainty have created a tough environment for newcomers, many of whom must stretch their budgets or make lifestyle compromises just to get a foot in the door, according to a new survey from Raleigh Realty.
The survey shows a clear generational divide in homeownership. The majority of first-time buyers are Gen X or Baby Boomers, while only 4% are Gen Z. For younger adults, especially Gen Z, the barriers to entry remain high. Those who do purchase tend to be higher earners—63% of Gen Z buyers make more than $75,000 annually. In contrast, many Baby Boomers bought their first homes with more modest incomes, suggesting that affordability has deteriorated over time.
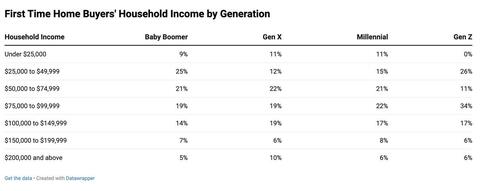
Income still plays a central role in homeownership access. While many first-time buyers earn between $50,000 and $75,000, a significant portion earn less, especially among older generations. Gen Z stands out again here, with relatively few buyers earning below $50,000. This trend reflects broader concerns among younger people about financial stability, shaped by growing up during the 2008 housing crash and entering adulthood amid pandemic-era economic turmoil.
Flexible work has had a strong impact on home buying decisions. A third of first-time buyers work remotely or in hybrid roles, and this flexibility often enables them to relocate in search of more affordable housing or better quality of life. Gen Z leads in remote work adoption, with more than 40% working fully in-office, while Baby Boomers represent the largest group not in traditional employment, instead relying on retirement income or alternative sources.
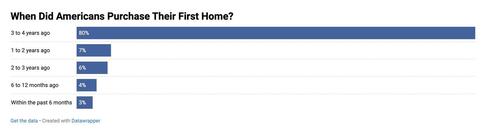
Despite media narratives about falling housing prices, very few first-time buyers made purchases in the last year. Most bought their homes three to four years ago, during or shortly after the pandemic housing surge. The steep drop in 2023 home sales reflects wider economic conditions, including high inflation and reduced affordability.
Single-family homes remain the overwhelming favorite among first-time buyers, with 90% choosing this option regardless of income. Even those earning less than $50,000 opted for standalone houses over condos or multi-family units. However, most chose existing homes rather than new construction, likely due to cost or availability.
For many, the journey into homeownership was taken solo or as a couple. Half of respondents were married, while 40% were single. Only a small percentage bought homes with friends, siblings, or unmarried partners. These results reflect traditional patterns of household formation and financial independence.
Most buyers moved quickly once they started looking for a home. About 70% closed within six months, and 35% found a home in three months or less. But speed didn’t reduce stress—90% of first-time buyers found the process difficult. The top source of stress was affordability, which overwhelmed concerns about mortgage approval, taxes, or maintenance.
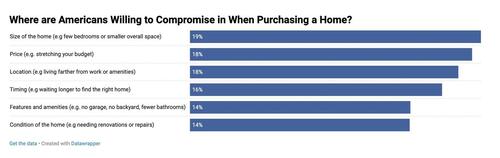
Financial strain led many buyers to make compromises. Nearly one in five settled for smaller homes, less desirable locations, or properties needing repairs. Stretching the budget was another common trade-off. Baby Boomers were most willing to go over budget, while Gen Z was most likely to compromise on location.
Concerns about job stability were widespread. More than half of buyers worried they wouldn’t be able to make mortgage payments if they lost their job, with the highest anxiety levels among Gen Z and Millennials. Baby Boomers, by contrast, were more confident in their financial resilience, likely due to retirement savings or paid-off homes.
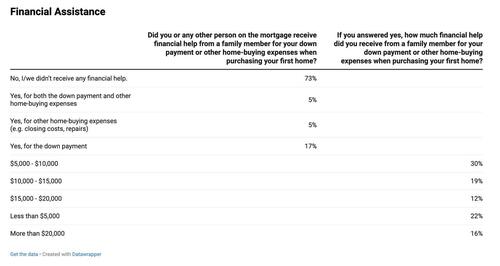
Contrary to popular belief, most first-time buyers didn’t receive financial help. About 73% paid for their homes without family assistance. Among those who did receive help, contributions varied, with 52% getting $10,000 or less. Just 16% received over $20,000, and only a small share received help from government programs.
The Raleigh Realty report says that even though mortgage approval is a common concern, most buyers didn’t apply for financing until after they began house hunting. Over half only applied to one lender. The majority selected lenders based on interest rates, while others went with banks they already used or those recommended by real estate agents.
Despite all these financial concerns, most buyers reported feeling satisfied after purchasing. While only 12% said they bought their dream home, 73% felt that homeownership brought them closer to the American dream. Lower-income buyers tended to report the highest satisfaction, possibly because expectations were more modest.
Few first-time buyers plan to move soon. Only 9% expect to sell their homes within five years, while nearly half intend to stay for at least a decade. A long-term mindset seems to dominate, with 30% planning to remain for 20 years or more.
Home improvement is a common post-purchase goal. Around 60% of buyers expect to invest $1,000 to $10,000 in upgrades during the first year, and nearly one in three plan to spend even more. These projects are seen as essential for adding value or addressing compromises made during the purchase process.
Younger buyers are also more likely to explore income-generating strategies. Around 40% of Gen Z and 30% of Millennials have taken on a second job to manage homeownership costs. Many also rent out parts of their property or use short-term rental platforms. In contrast, only 14% of Baby Boomers supplement their income in this way.
Emergency savings are more common among first-time buyers than the general population. Around 79% reported having some form of savings, with most holding over $1,000 and 17% saving more than $20,000. Younger buyers may be more motivated to save due to fears about job loss or economic instability.
In summary the full survey results show that while homeownership is still viewed as an important milestone, today’s first-time buyers are navigating a complex and stressful landscape. Income, generational experience, and work flexibility all influence outcomes, and most buyers are willing to make sacrifices to achieve the goal of owning a home.
Tyler Durden
Thu, 05/08/2025 – 05:45

 4 miesięcy temu
4 miesięcy temu